The often discussed but seldom implemented 360-degree customer view presents a holistic customer profile record, capturing all kinds of customer data coming from the systems and channels, aggregating it to determine what’s interesting for the customers and applying the insights to develop and provide engaging and personalized customer experiences and achieve company strategic goals. It all may sound so easy, but it is not. Gartner says that less than 10% of the organizations have a 360-degree customer view, out of which, merely 5% use it properly to systemically expand their business.
360-Degree Customer View Intelligence
First, the 360-degree customer view derives the customer intelligence, displaying the customer insights that suggest how to solve for a customer, upsell, delight and retain the customer, as well as deliver personalized, contextual, relevant and predictive customer experiences.
360-Degree Customer View Predictive Analytics
Second, the 360-degree customer view forms the basis of predictive analytics. A 360 view takes records of all customers’ interaction and helps to determine the action to be taken for each customer.
Each customer interaction is related to the business performance objective, as an increase in the customer share, retention or loyalty. Telecom customers are highly heterogeneous (having diverse preferences), so telecom businesses must develop that actions as per the customer interaction record and then scale up those actions for defined future outcomes.
For instance, determining and evaluating the outcomes of the advertisements, sales proposals, marketing offers, cross-sell offers, customer service responses or loyalty program promotions for every customer segment enables the business to regulate and direct its messaging and actions with more specificity for better and predictable outcomes.
The capability to determine and predict the customer responses to the company actions would help in customer acquisition and retention, and this capability is gained through 360-degree customer view.
360-Degree Customer View Segmentation
Third, the 360-degree view prescribes customer alignment, mapping each customer into various customer segments to allocate the resources and align the business processes on the basis of customer contribution and other business drivers. For instance, a telecom service provider may provide high-touch customer support (with Service Level Agreements, entitlements, etc.) for high contribution customers and self-service support for the low contribution, individual customers.
Defining the business processes in terms of customer segment is very effective in growing the margins and revenues from high contribution customers and decreasing the costs to serve low or maybe negative margin customers.
The below figure reflects how the companies can make use of the segmentation to align business processes and services, to pursue 360-degree customer view strategy:
Telecom Company Customer Segmentation Scenario
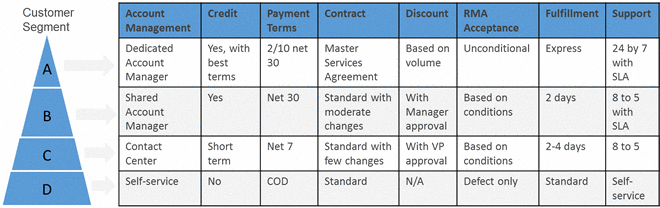
In the example above, the customers have been segmented as per profit; from most profitable to least profitable. The Customers at point “A” are the most profitable customers for which the company has assigned a dedicated account manager, while at point “D”, the customers are least profitable for whom the company is offering the self-service facility. This is a form of customer 360-degree view in terms of revenue customers give to the company, how fast they give revenue to the company and what kind of service the company gives to each of these customer segments.
Identifying the customers contributing a negative margin to the business makes an opportunity to plug that profit leakage. Decreasing the cost for serving these customers leads to an alternative to discontinuing these customer relationships.
Aside from these, the 360-degree view brings other benefits like cross departmental data sharing and business process synchronization. For instance, sales might be wiser to defer some new promotion to a customer already waiting on a critical customer service response. When designing the cross-departmental customer interactions, it is important to keep into account that customers expect a seamless and unified experience irrespective of the company division they engage.
360 Degree Customer View – Data Types to Consider for Segmentation
Customer segmentation makes an essential best practice when it comes to customer relationship management. However, many businesses do mistake in customer segmentation by grouping the customers as per their upside potential to the business and without knowing what these customers want from the business. Engaging the customers in a one to one manner at scale is best attained by developing finely tuned customer segments and further affixing customer profiles with these data types:
-
Demographic data
Demographic data like customer size, type, location, and industry form the initial basis for the customer segmentation. While demographics make the starting point, they are comparatively stagnant, and thus, not good predictors of the customer behaviors and contribution to the key performance measures like revenues, profits, costs, and lifetime value.
-
Transaction data
A CRM best approach is to attach customer profiles with their financial transaction data for reallocating the investment and efforts to customers on the basis of their contribution to the business. The fastest way to an uplift in profits is to invest the bulk of the company services into the most profitable customers. Financial transaction data usually include sales, referrals, returns, and costs to serve.
-
Environmental data
The 5% of businesses leveraging on their customer 360-degree view to expand their businesses usually consider environment data for their customer profile creation. This data is also called economic third-party data and may include profession, personal income, education, family size, home value, household income, net worth, economic affluence, disposable income, and even retail purchases records or travel expenses.
-
Behavioral data
The improved customer intelligence, obtained from this data, vividly improves customer segmentation and their profile records with dimensions and traits that more precisely predict demand and intent, and lead to advanced segmentation techniques like micro-targeting and campaign triggers. Moreover, this improved segmentation helps companies deliver better offers that are more relevant, personalized, and timely; all features that considerably improve customer engagement and conversions.
-
Social data
As customers are now more prolific in the social channels, businesses can listen and decide upon this data for relationship building and engagement purposes. Social data let businesses understand the customers’ sociological attributes by their ‘Likes’, retweets or comments, which eventually forms the customer social graph.
Conclusion
Generating a 360-degree customer view is closely linked to customer segmentation and profiling. Moreover, the record of each customer’s interaction with the company also matters to determine the most profitable and least valuable customers. The discussion that we had in this article reflects the strategic value of integrating the finely tuned customer segmentation strategy with the customer profile record gained across multiple touchpoints that disclose each customer’s DNA. Altogether, it creates a more accurate 360-degree customer view.
BBI Consultancy is a digital transformation consulting firm that offers Enterprise Data Management solutions, Digital transformation solutions, Data protection solutions, big data services and more. join the digital revolution, get in touch with BBI. We are based in multiple locations across the globe, including Egypt, UAE and KSA.